Modelling Intra-Axonal Heterogeneity
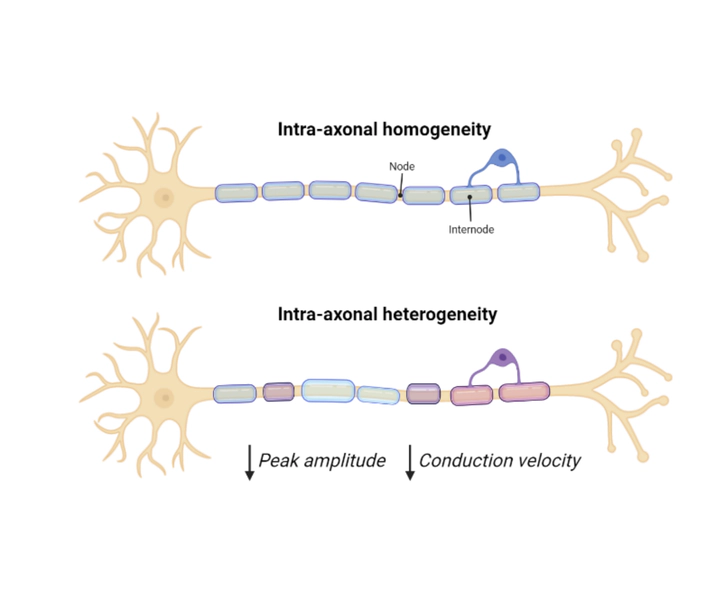 Figure created with BioRender.
Figure created with BioRender.Investigating the impact of myelination variations along a single axon on action potential (AP) conduction.
Summary
Background
- Myelination is crucial for rapid and efficient nerve signal propagation.
- Traditional models assume uniform myelination, but recent findings suggest significant variability along axons.
Materials and Methods
- We used a double-cable computational model.
- We analysed variations in internode length, myelin thickness, and periaxonal space width.
- We conducted simulations in MATLAB to observe effects on AP conduction velocity and amplitude.
Results
- Individual variations in internode length, myelin thickness, and periaxonal space width alone do not significantly impact AP properties.
- Combined variations of these parameters significantly reduce conduction velocity and peak amplitude.
Conclusion
- Incorporating intra-axonal heterogeneity into computational models is essential for accurately representing neuronal signal conduction.
- These findings have implications for understanding both normal neuronal function and demyelinating disorders.